Confusing words – Part 1
Similar words that can be difficult to use correctly in English! Mistakes are common when there are no exact equivalents in your native language, or when rules on usage differ. Let’s look at the differences between those words below by explaining how each word is used separately.
1. Look at, see or watch
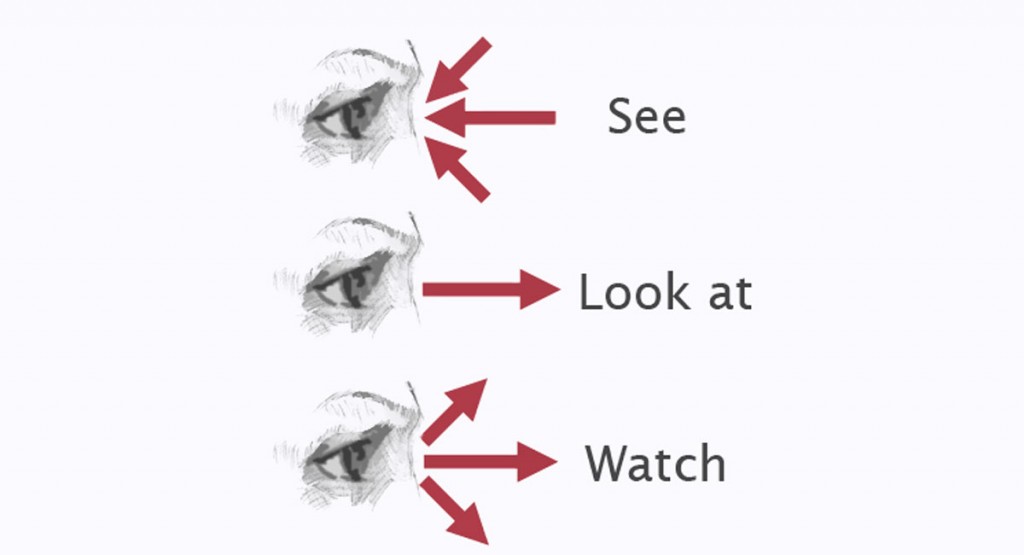
Look at: When we look at something, we direct our eyes in its direction and pay attention to it:
Examples: Come and look at this photo Carina sent me.
– Look at the rabbit!
Warning: When look has an object, it is followed by ‘at’:
Examples: Look at the rain. It’s so heavy.
Not: Look the rain.
See: See means noticing something using our eyes. The past simple form is saw and the -ed form is seen:
Examples: I saw Trevor at the shopping centre yesterday.
– Has anyone seen my glasses?
Watch: Watch is similar to look at, but it usually means that we look at something for a period of time, especially something that is changing or moving:
Examples: We watch television every evening.
– I like to sit at the window to watch what’s happening in the garden.
Warning: We use see, not watch, when we talk about being at sports matches or public performances, such as films, theatre and dramas. However, we watch the television:
Examples: We saw a wonderful new film last night. You’ll have to go and see it while it’s in the cinema.
Not: We watched… You’ll have to go and watch …
2. Bring vs. take
Bring: Describes the movement toward someone or something.
Examples: I’ll bring some coffee.
– Sam will bring his books to class.
– Remember to bring me a souvenir from from your trip.
Take: Describes the movement away from someone or something.
Examples: Take the coffee cups back to the kitchen
– Remember to take out the trash.
– I’ll take the dog out for a walk.

We can use the same rule for: COME & GO
Example: Come here, please. vs. Go there, please.
Come inside. vs. Go outside.
Sam comes from America. vs. Sally goes to school.
3. As vs. like
As and like are prepositions or conjunctions. The prepositions as and like have different meanings. As + noun means ‘in the role of’, like + noun means ‘similar to’ or ‘in the same way as’.
Example: As your father, I’ll help you as much as I can. –> The speaker is the listener’s father.
– Like your father, I’ll help you as much as I can. –>The speaker is not the father but wishes to act in a similar way to the father.
Warning 1: We use like (but not as) to compare two things:
Example 1: She’s got a headache like me.
Not: She’s got a headache as me.
Example 2: Like the other students, he finds it a bit difficult to get to lectures early in the morning.
Not: As the other students, he finds it …
Warning 2: When we compare appearance or behaviour, we use like, not as:
Example: That house looks like a castle.
Not: That house looks as a castle.
Warning 3: As is commonly used to talk about jobs:
Example: He worked for a long time as a teacher in Africa.
Not: … like a teacher in Africa.
Warning 4: The conjunctions as and like have the same meaning when used in comparisons. Like is a little more informal.
Example: Nobody understands him as I do.
– Nobody understands him like I do.
4. Fun vs. Funny
Fun is an uncountable noun meaning ‘pleasure and enjoyment’:
Example: We had such fun together.
– It was fun to go to the beach with Rita’s family.
– I hope you have fun!
Funny is an adjective and it means ‘amusing’ or ‘causing laughter’:
Example 1:
A: How would you describe Lorna?
B: Well. I think she’s very self-confident and assertive. I think she’s genuinely funny.
Example 2: I think Jerry Springer is so funny. I just laugh so much when I watch his show.
Funny can also mean ‘strange’, ‘surprising’, ‘unexpected’ or ‘difficult to explain or understand’
Example: A funny thing happened to me the other day. I was parking my car and a man came and knocked on my window … (A strange/surprising/unexpected thing happened …)
– Wasn’t it funny the way Don just got up and left without saying goodbye to anyone? (Wasn’t it strange …)
5. Say, tell, speak or talk

Say: When we use ‘say’, we do not use an object (e.g. me/them/you) immediately after the verb. The verb ‘say’ is used when we quote people directly and also when we give instructions.
Example: Amelia said she would be back soon.
– The weatherman said it would rain today.
– I won’t say this again! – Will you please get ready for school now?
Say can also be used to express an opinion or thought, as in: ‘I say we should give each person twenty tickets each to sell.’
Tell: When we use ‘tell’, we also include the object (e.g. you/her/us) immediately after the verb. The verb ‘tell’ is used when we say something to someone, and is commonly used when giving an order or instruction.
Example: I told my son to brush his teeth.
– The teacher told the class to do their homework.
– You forgot to tell me to bring my swimming costume!
Sometimes ‘say’ and ‘tell’ can be used interchangeably to express the same meaning when information is being passed from one person to another. In this case, the construction would be: ‘tell’ + object or ‘say’ + ‘to’ + object.
Example: Laura told me that she would be late for work.
– Laura said to me that she would be late for work.
Warning: ‘He said me…’ or ‘She said me that…’ is incorrect. Remember to include ‘to’ between ‘said’ and the object! Just as you would ‘send a letter TO someone’, you would also ‘say something TO someone’. The preposition ‘to’ shows the direction in which the information is going.
Speak: We use the verb ‘speak’ (instead of ‘talk’) when we are in a more formal situation and wish to emphasise that something is important. When ‘speak’ is used as a noun (speech) it also takes on a more formal tone that when we use ‘talk’ – i.e. ‘Give a speech’ is more formal than ‘give a talk’.
Example: We need to speak about your attendance this term! (stricter than ‘talk about’)
John will be speaking at an international conference next month. (more prestigious than ‘give a talk on…’)
We can also use ‘speak’ to describe verbal fluency or knowledge of languages, as in: ‘He speaks three languages fluently – German, French and Spanish.’. In this context, ‘speak’ simply means that the person knows the languages. It doesn’t only refer to spoken ability.
Talk: We use the verb ‘talk’ when we are in a more relaxed setting or when we are among friends in a conversational situation. You can think of ‘talk’ as a slightly more formal word for ‘chat’.
Example: Sorry, who were you talking to before I interrupted?
– I was talking with my mum the other day and we decided that…
– I love chatting with my mates (friends) over a cuppa (cup of tea)!’ (very informal)
Often ‘speak’ and ‘talk’ can be used interchangeably to give the same meaning and there is no need to change the grammar of the sentence.
Example: I will speak/talk with you about this more on Monday.
– We can speak/talk about the new project next week.


Leave a Reply